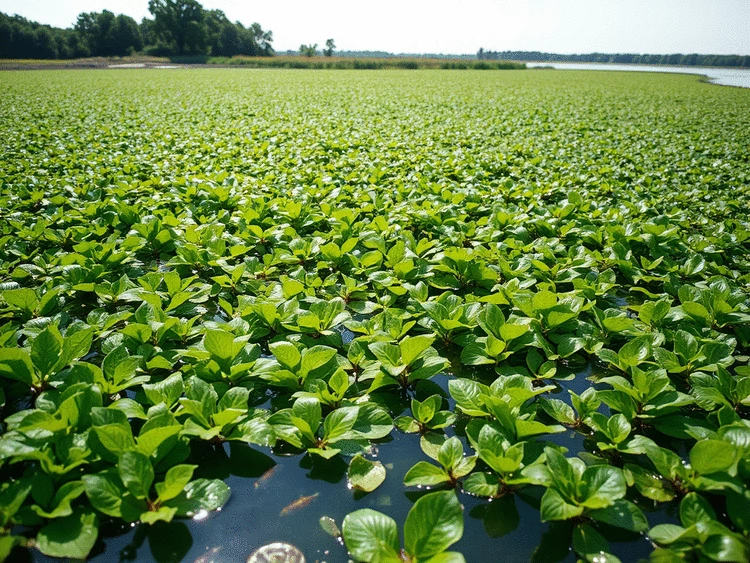
What if I told you that a single aquatic plant could significantly disrupt local economies and ecosystems? The invasive hydrilla is not just a nuisance; it's a formidable opponent that can wreak havoc on waterways and the communities that depend on them. Understanding its impact is crucial for environmental and economic resilience.
What You Will Learn
- Hydrilla can grow up to an inch per day, quickly choking out native species and disrupting ecosystems.
- The economic costs of hydrilla infestations include increased maintenance for waterways and lost revenues from tourism.
- Recreational activities suffer due to hydrilla, leading to declines in local business revenues and community events.
- Property values can decrease near infested waterways, impacting local tax revenues and community investment.
- Effective hydrilla management requires proactive strategies, community involvement, and integrated approaches for sustainability.
Economic Impact of Hydrilla Infestations
Hydrilla, a fast-growing aquatic plant, poses significant economic and ecological threats. Its rapid spread impacts waterways, infrastructure, tourism, property values, and fisheries, leading to substantial costs for control and mitigation.
Reduced Water Flow & Infrastructure Challenges
- Increased dredging & maintenance costs.
- Damage to irrigation & treatment facilities.
- Potential flooding risks.
Recreational Losses & Tourism Impact
- Decline in fishing licenses & business revenues.
- Reduced tourism due to unattractive waters.
- Loss of water-centric community events.
Decline in Property Values
- Impacts local tax revenues.
- Buyers avoid affected locations.
- Difficulty securing mortgages.
Effects on Fisheries & Agriculture
- Reduced fish populations & commercial opportunities.
- Compromised water quality for crops.
- Increased native-invasive species competition.
Understanding the Economic Impact of Hydrilla Infestations
As an aquatic biologist with years of experience studying invasive species, I’ve seen firsthand how invasive plants, particularly hydrilla, can wreak havoc on local ecosystems. Hydrilla is not just another aquatic plant; it's a formidable opponent that can clog waterways and disrupt the balance of our aquatic environments. But what exactly makes hydrilla such a serious threat?
What is Hydrilla and Why is it a Threat?
This fast-growing aquatic plant can spread rapidly, forming dense mats that choke out native species and interfere with recreational activities. Its ability to thrive in various water conditions means that it can invade lakes, rivers, and wetlands, sometimes without a trace until it's too late. Have you ever noticed how swiftly certain plants take over a garden? Imagine that, but on a much larger, more destructive scale.
- Hydrilla can grow up to an inch per day!
- It reduces light penetration in water bodies, harming native plants.
- Its dense growth can lead to oxygen depletion, affecting fish and other aquatic life.
This aggressive growth not only disrupts ecosystems but also poses serious economic challenges to communities that depend on healthy waterways. It's a vicious cycle that affects local biodiversity and economic stability!
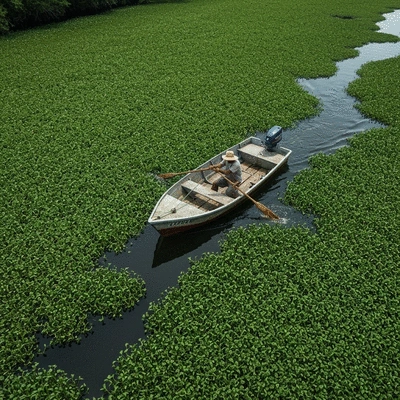

Key Economic Damages Linked to Hydrilla Growth
The economic impact of hydrilla is substantial and multifaceted. Many communities find themselves grappling with costs associated with control measures, lost revenue from tourism, and declining property values. Let's break down some of the primary areas affected by hydrilla infestations:
Reduced Water Flow and Infrastructure Challenges
One of the most significant issues is how hydrilla can obstruct water flow in rivers and man-made canals. This blockage can lead to increased maintenance costs for local authorities. Think of it as trying to pour water through a clogged kitchen sink—frustrating and costly!
- Increased expenses for dredging and maintenance of waterways.
- Infrastructure damage to irrigation systems and water treatment facilities.
- Potential flooding risks due to reduced water carrying capacity.
Communities can find themselves in a financial bind, trying to address problems that hydrilla has caused while also needing to invest in solutions to restore infrastructure.
Recreational Losses and Impact on Tourism
Hydrilla's presence can deter visitors looking to enjoy recreational activities such as fishing, boating, and swimming. When aquatic environments become overrun with this invasive plant, the decline in recreational usage translates directly into lost income for local businesses. Have you ever visited a beautiful lake only to be put off by its murky and uninviting conditions? That's the reality for many affected areas.
- Decline in fishing licenses sold and local business revenues.
- Reduced tourism due to unattractive water conditions.
- Loss of community events and activities centered around water sports.
When we neglect to control hydrilla, we not only harm our ecosystems but also the economy that thrives on them!
Decline in Property Values and Its Ripple Effects
As the presence of hydrilla affects the quality of nearby water bodies, property values can also take a hit. Homeowners near infested waterways might struggle to sell their homes, leading to a wider economic downturn in the community. It’s a ripple effect that can damage not just individual fortunes but entire neighborhoods as well.
- Property values may decrease, impacting local tax revenues.
- Potential buyers may avoid locations with known hydrilla issues.
- Increased difficulty in securing mortgages for properties near infested waters.
This downward spiral can create lasting impacts on community investment and development efforts.
Effects on Fisheries and Agriculture
Finally, hydrilla can severely impact local fisheries by disrupting habitats for fish and other aquatic organisms. Additionally, agricultural operations that rely on clean water sources can suffer from the spread of this invasive plant, leading to reduced crop yields and increased costs. Have you considered how interconnected our agricultural practices are with our aquatic ecosystems? The health of our fisheries directly impacts food security and local economies.
- Reduced fish populations leading to decreased commercial fishing opportunities.
- Compromised water quality affecting irrigation for crops.
- Increased competition for space and resources between native and invasive species.
These effects highlight the crucial need for effective management of hydrilla to protect not just our ecosystems, but also our economic resilience.
The Role of Aquatic Weeds in Ecosystem Disruption
Hydrilla is a prime example of how aquatic weeds can disrupt not only local ecosystems but also the economy that depends on them. By understanding the economic impact of hydrilla infestations, we can take informed steps toward managing its spread. It's essential for environmental professionals, educators, and community members alike to join forces in this battle. After all, protecting our waterways is vital for ensuring a healthy economy and a thriving ecosystem!
We Want to Hear From You!
How do you think hydrilla infestations have impacted your local waterway? Share your thoughts below:
Frequently Asked Questions About Hydrilla and Its Economic Impact
Q1: What is hydrilla and why is it considered a threat?
Hydrilla is a fast-growing invasive aquatic plant that forms dense mats, choking out native species and interfering with recreational activities. It's a threat because it rapidly spreads, disrupts ecosystems, and causes significant economic damage to communities.
Q2: How does hydrilla impact local economies?
Hydrilla impacts local economies in several ways: increasing maintenance costs for waterways, reducing tourism and recreational revenues, decreasing property values near infested areas, and negatively affecting fisheries and agriculture.
Q3: What are the infrastructure challenges caused by hydrilla?
Hydrilla obstructs water flow in rivers and canals, leading to increased dredging and maintenance costs. It can also damage irrigation systems and water treatment facilities, and contribute to potential flooding risks due to reduced water carrying capacity.
Q4: How does hydrilla affect tourism and recreational activities?
Dense hydrilla mats make waterways unattractive and unusable for activities like fishing, boating, and swimming. This deters visitors, leading to a decline in local business revenues, reduced sales of fishing licenses, and the cancellation of water-centric community events.
Q5: What are the long-term management strategies for hydrilla?
Effective management requires proactive intervention, integrated approaches combining various control methods, and strong community involvement. Future efforts should focus on innovative technologies, sustainable practices, and inter-agency collaboration to prevent its spread and mitigate its impact.
Summarizing the Economic Costs and Benefits of Hydrilla Control
As we've explored the economic implications of hydrilla infestations, it's clear that the costs of inaction can far outweigh the expenses associated with effective control measures. By investing in management strategies, we can not only mitigate the immediate damages but also pave the way for healthier ecosystems. Understanding the balance of costs and benefits is crucial for decision-makers, and it's a topic I am passionate about as the founder of the Hydrilla Conservation Initiative.
Through this initiative, we have worked tirelessly to provide resources and insights that help environmental professionals and educators understand hydrilla's economic impact. So, what are the key takeaways when it comes to managing hydrilla infestations?
Key Takeaways on Managing Hydrilla Infestations
- Proactive Management: Early intervention can dramatically reduce long-term costs. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, for example, explores various methods, including the use of herbicides like Diquat, for effective management, as detailed in their outreach meeting materials.
- Integrated Approaches: Combining several control methods improves effectiveness and reduces reliance on any single strategy.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local stakeholders can enhance awareness and support for management efforts.
These takeaways not only highlight the importance of hydrologic stewardship but also resonate with our mission to empower communities in their fight against invasive species. Have you considered how your involvement could make a difference in your local ecosystem?
Future Directions for Research and Policy Development
The landscape of invasive species management is ever-evolving. To stay ahead of hydrilla’s proliferation, we must focus on innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. This means investing in research and developing policies that reflect the dynamic nature of our ecosystems. Here are some promising areas for future focus:
- Innovative Technologies: Researching advanced monitoring tools and selective herbicides can improve our ability to manage hydrilla. For instance, Pennsylvania Sea Grant provides fact sheets on invasive aquatic species like hydrilla, offering valuable insights into identification and control methods.
- Sustainable Practices: Long-term strategies that promote ecosystem resilience are essential for ongoing success.
- Collaboration: Inter-agency coordination ensures efficient use of resources and knowledge sharing.
As I continue my work in aquatic biology, I am excited about the potential of these developments to transform our approach to controlling hydrilla and other invasive species. The collaborative efforts we can foster at local, state, and national levels will be pivotal in overcoming these challenges.
Taking Action: What You Can Do
Now that we've dissected the economic impact and future directions for managing hydrilla, let’s discuss how you can get involved! Collective action is key to making a sustainable difference in our ecosystems.
Engaging with Local Initiatives and Research
One of the most effective ways to combat hydrilla infestations is to connect with local initiatives. Participating in local research projects or community clean-up days not only helps restore your natural areas but also fosters a sense of connection and responsibility within your community. Have you looked into local conservation groups in your area? You might be surprised by the opportunities available!
Advocating for Effective Hydrilla Management Policies
Advocacy plays a crucial role in shaping the policies that govern our waterways. By getting involved in local government meetings or environmental organizations, you can voice your concerns and push for better strategies to manage invasive species like hydrilla. Your input matters, and it can lead to significant changes in how we protect our ecosystems.
Community Awareness and Educational Outreach on Hydrilla Impacts
Education is a powerful tool in the fight against invasive species. Sharing information about the impacts of hydrilla and the importance of management can inspire action within your community. Whether it’s through workshops, local events, or social media, spreading awareness can unite and empower individuals to take steps toward environmental stewardship.
Engaging with the Hydrilla Conservation Initiative can provide you with the resources needed to champion these causes effectively. Together, we can make strides in preserving our vital waterways for future generations!
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Hydrilla can grow up to an inch per day, threatening local ecosystems.
- Invasive hydrilla leads to reduced water flow, increased maintenance costs, and potential flooding.
- Tourism and recreational activities decline due to unattractive water conditions caused by hydrilla.
- Property values decrease near infested waterways, impacting local economies.
- Effective hydrilla management requires proactive, integrated approaches and community involvement.







